Loading...
Loading...
Information & Cybersecurity Service Offerings
As innovation accelerates and connectivity increases, enterprises are more exposed to sophisticated cyberattacks. It's essential to integrate cybersecurity throughout the technology framework and business lifecycle. Information and cybersecurity refer to the practices, technologies, and processes designed to protect data, networks, programs, devices, and systems from digital attacks, damage, or unauthorized access. These disciplines are crucial for safeguarding the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information technology systems and data. At Big Blue Infotech, we have experienced security professionals to offer Information and Cybersecurity solutions that address the key challenges faced by enterprises today. Our security services aim to improve the agility, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness of the next generation needs of information security and compliance programs.
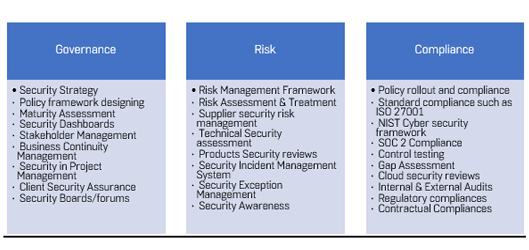
Please note that this is not an exhaustive list of the GRC services we provide. We can tailor our services to meet the specific needs of our Clients.

